THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
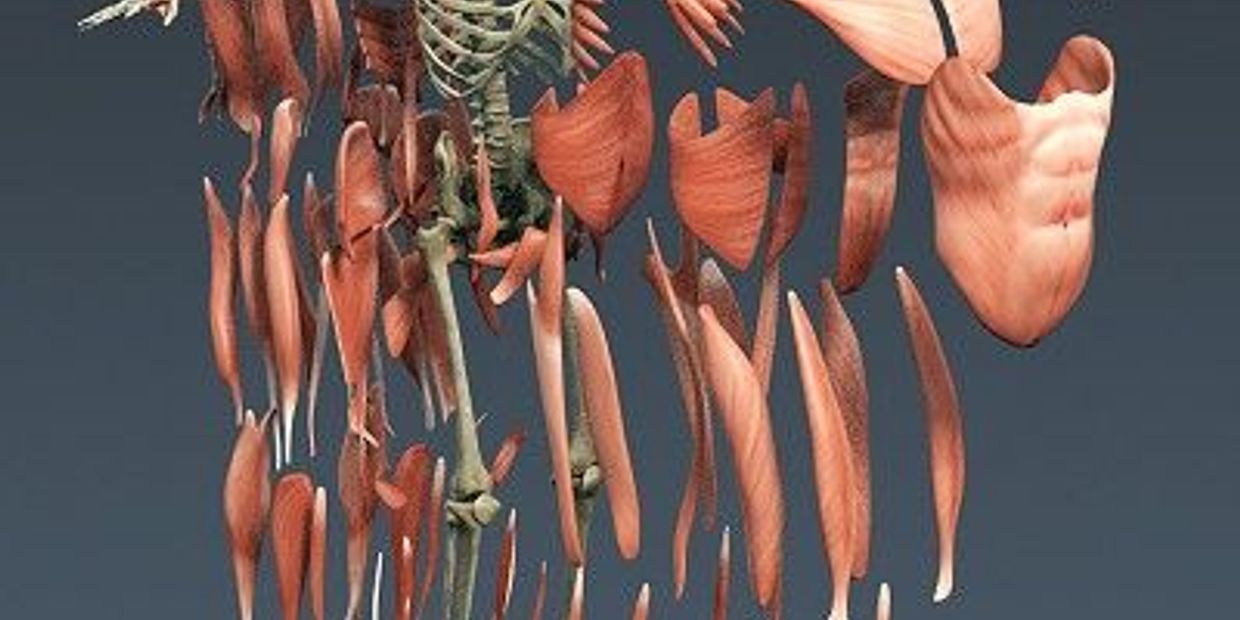
Introduction
The muscle system represents a tissue structure consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. This constitutes body balance, regulates posture, and circulates oxygen all over the body. The vertebrate muscle system is regulated by the nervous system, while certain muscles (such as the cardiac muscle) can be completely autonomous. It forms the musculoskeletal structure along with the skeletal system, which is responsible for human body movement. There are three distinct muscle types:
- skeletal muscles,
- heart, or cardiac muscles
- smooth (non-striated) muscles.
The muscles provide the body with:
- energy,
- coordination,
- stance,
- motion and heat to keep it warm.
Skeletal muscles execute a synchronized contraction when activated by an action potential, by shortening each sarcomer (complex unit of striated muscle tissue).
The moving filament model of muscle contraction is the latest theoretical mechanism for understanding contraction.
Actin and myosin fibers interact with each other in a contractile motion. Myosin filaments have heads that are club-shaped and expand into the actin filaments.
More substantial structures along the myosin filament called myosin heads are used to provide the actin filaments with attachment points to binding sites.
The myosin summits move in a synchronized manner, swing towards the sarcomer's core, disconnect and then re-attach to the actin filament's closest binding site.
It is known as a drive style rachet device.
This cycle absorbs significant quantities of Triphosphate Adenosine (ATP).
Energy for this comes from ATP, the cell's energy supply. ATP connects the myosin heads and actin filaments to the cross-bridges.
The release of energy triggers the swiveling of the myosin head.
Muscles retain no ATP, and so the discharged molecule of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) must be quickly recycled into ATP.
Muscle tissue also includes a stored supply of a fast-acting recharge material, creatine phosphate that may initially assist in generating ADP's rapid regeneration into ATP.
For each sarcomere cycle, calcium ions are necessary. When a muscle is forced to contract, calcium is absorbed from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcomere. This calcium uncovers the attachment sites for the actin.
The calcium ions are expelled from the sarcomer and back into storage in the sarcoplasmic reticulum as the muscle no longer has to contract.
Aerobic and Anaerobic muscle activity
At resting, the body aerobically stores much of the ATP within the mitochondria [an organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur. It has a double membrane, the inner part being folded inwards to form layers (cristae)] without developing lactic acid or any other fatiguing byproducts.
The form of ATP development during exercise varies based on the individual's health as well as the length and severity of the exercise.
At lower levels of activity, energy is created aerobically by mixing oxygen with carbohydrates and fats accumulated in the body when exercise occurs for a long period of time (several minutes or longer) ATP development will turn to anaerobic pathways, such as the use of creatine phosphate and the phosphagen mechanism or anaerobic glycolysis, which is greater in intensity, with potential length declining as intensity increases.
Aerobic ATP synthesis is much slower biochemically and can only be used for the long-lasting, low-intensity activity, but does not create fatiguing waste products that can not be eliminated from the sarcomer and body quickly, resulting in a much greater amount of ATP molecules per fat or carbohydrate molecule.
Aerobic preparation calls for a more effective oxygen delivery system, enabling aerobic metabolism to commence prompter.
The development of anaerobic ATP produces ATP much faster and allows for near-maximum intensity exercise, but also provides significant amounts of lactic acid to make high-intensity exercise unsustainable for more than several minutes.
The phosphagen mechanism is also anaerobic, it makes the maximum rates of exercise strength, but intramuscular phosphocreatine (also known as creatine phosphate (CP) or PCr (Pcr), is a phosphorylated creatine molecule that serves as a rapidly mobilizable reserve of high-energy phosphates in skeletal muscle, myocardium and the brain to recycle adenosine triphosphate, the energy currency of the cell) reserves are minimal. They can only supply energy for workouts lasting up to 10 seconds.
Recovery is speedy, with completely regenerated creatine stores within five minutes.
Cardiac muscles
The muscles of the heart are different from skeletal muscles since the muscle fibers are laterally related.
Sometimes, as the rigid muscles, they don't control themselves.
Heart muscles are regulated by the autonomic nervous system-mediated sinus node.
Smooth muscles
Smooth muscles are actively regulated by the adaptive nervous system and are unconscious; therefore, they are unable to be affected by conscious thinking.
Functions such as heartbeat and lungs (which can be managed voluntarily, be it to a small degree) are unconscious movements that are not smooth muscles.
Skeletal muscles
Approximately 639 skeletal muscles are found in the human body.
Muscle contraction regulation
Neuromuscular junctions are the focal point at which a motor neuron binds to a muscle.
Acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter involved in the relaxation of the skeletal muscle) is released from the nerve cell's axon terminal as an action potential hits the microscopic junction, called a synapse.
A community of chemical messengers cross the synapse and induce the development of electrical changes that are produced in the muscle cell when the acetylcholine binds on its surface to receptors.
Calcium is produced in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the cell from its storage area.
An impulse from a nerve cell triggers calcium release, which results in a simple, quick contraction of the muscle called a twitch.
When a question occurs at the neuromuscular junction, there may be a very extended contraction, tetanus.
A lack of balance at the junction may also cause paralysis.
Skeletal muscles are divided into hundreds of motor units, each of which has a motor neuron connected to it by a set of small finger-like structures called axon ends.
These attach to and control the discrete bundles of muscle fibers.
A structured, fine-tuned approach to a given situation may require monitoring the precise number of engine units used.
Although individual units of muscle contract as a unit, due to the motor unit structure, the whole muscle may contract on a predetermined basis.
Coordination, stability, and regulation of motor units also fall under the influence of the brain's cerebellum.
This allows intricate muscle control with little concerted effort, for example, while driving a car without worrying about the process..
TRADITIONAL MEDICINE
Herbs & Essential Oils
Passionflower (Passiflora incarnata)
Passionflower (Passiflora incarnata)
Passionflower (Passiflora incarnata)

Known also as passionflower, is a very attractive plant, which has numerous properties, its petals containing phytosterol and flavonoids, both substances having antioxidant effects.
It also contains alkaloids, essential oils, and other ingredients with soothing/calming and analgesic effects. It is used to treat insomnia, muscular contractions, stress, anxiety, etc. It can be consumed in the form of infusion.
Passion flower is a climbing vine that is native to the southeastern United States, and Central and South America. It was used as a food plant and in traditional medicine as a sedative. The above ground parts are used to make medicine.
Passion flower is taken by mouth for sleep problems (insomnia), anxiety, adjustment disorder, indigestion, pain, fibromyalgia, muscle cramps, diarrhea, relieving symptoms related to narcotic drug withdrawal, and reducing anxiety and nervousness before surgery.
Lavender ( Lavandula angustifolia )
Passionflower (Passiflora incarnata)
Passionflower (Passiflora incarnata)

Lavender has numerous properties, helping to treat many other diseases.
The lavender oil is known for its efficiency and relaxing the musculature.
It also relieves pain and inflammation.
Lavender is an herb native to northern Africa and the mountainous regions of the Mediterranean. It is also grown for the production of its essential oil, which comes from the distillation of the flower spikes of certain lavender species. The oil has cosmetic uses, and it is believed to have some medicinal uses.
The anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in Lavender oil are quite effective for treating pains that arise from muscle stress and tension. Lavender oil can also ease swelling and improve blood circulation. It is excellent for relieving the muscle spasm caused by mental stress and anxiety.
Everlasting flowers (Helichrysum)
Passionflower (Passiflora incarnata)
Everlasting flowers (Helichrysum)

The Helichrysum flowers are often called the Eternal Flower or Immortelle, possibly because it has been used for centuries as an essential oil.
Helichrysum has been used in herbal medicine to help all manner of illnesses in various cultures.
Many accounts also suggest the Greek Gods were given the
Helichrysum flowers because of all the advantages that it possesses.
The power of Helichrysum to relax the skin and decrease the amount of inflammation and redness is the primary reason that this essential oil is of prime importance.
Being an anti-inflammatory also means that this mineral oil should be used in one's body to reduce discomfort, whether it is a fever or muscle pain.
Eucalyptus
Eucalyptus
Everlasting flowers (Helichrysum)

Eucalyptus is a fast-growing evergreen tree native to Australia. As an ingredient in many products, it is used to reduce symptoms of coughs, colds, and congestion. It also features in creams and ointments aimed at relieving muscle and joint pain.
The oil that comes from the eucalyptus tree is used as an antiseptic, a perfume, as an ingredient in cosmetics, as a flavoring, in dental preparations, and in industrial solvents.
Chinese, Indian Ayurvedic, Greek, and other European styles of medicine have incorporated it into the treatment of a range of conditions for thousands of years.
There are over 400 different species of eucalyptus. Eucalyptus globulus, also known as Blue Gum, is the main source of eucalyptus oil used globally.
Leaves are steam distilled to extract the oil, which is a colorless liquid with a strong, sweet, woody scent. It contains 1,8-cineole, also known as eucalyptol.
The leaves also contain flavonoids and tannins; flavonoids are plant-based antioxidants, and tannins may help to reduce inflammation.
Juniper
Eucalyptus
Wild Thyme

Juniper is a short to medium-height tree that grows wild in some parts of Europe, North America, and Asia. There are many varieties of juniper, but Juniperus communis is the most common in North America.
People use the juniper berry to make medicine. Medicinal preparations include the extract of juniper berry, as well as the essential oil of juniper berry.
Juniper Berry (Juniperus communis) essential oil is an excellent choice for relieving muscle and joint pain when applied topically. It is pain-numbing and encourages circulation, which also makes this oil useful for acne.
Wild Thyme
Eucalyptus
Wild Thyme

Thyme was one of Hippocrates’ 400 simples or remedies. In Greece, infusions of the herb were drunk at the end of banquets for digestive purposes, and offerings of it were made to Venus and other divinities.
The name thyme comes from the Greek word thymon, or strong odor, because of its fragrance.
It was also used by the ancient Egyptians who called it tham, and used it in embalming. More recent research has proved the anti-fungal and anti-bacterial effect of the plant.
Thyme has anti-inflammatory properties: as per research, thyme contains several anti-inflammatory properties which are effective in preventing chronic inflammation in the body.
It has also been beneficial in the treatment of muscle cramps: one of the top health benefits of thyme is its effectiveness in treating menstrual cramps and other types of spasms in the body.
Valerian
Chamomile
Chamomile

Valerian is a perennial plant. It has pink flowers. It grows in North America and Europe. The medicinal part is made from the fresh underground roots that have a strong smell.
Valerian root has 2 types of compounds. The both have sedative effects. These compounds include sesquiterpenes (valerenic acid) and iridoids triesters (valepotriates).
Valerian may have a sedative effect. It may have a stimulant effect for extreme fatigue. Valerian root may lower blood pressure and relax muscles.
Some women use valerian for menstrual cramps and symptoms associated with menopause, including hot flashes and anxiety.
Chamomile
Chamomile
Chamomile

Chamomile is an ancient herb that’s used to treat a variety of ailments, including muscle spasms.
It contains 36 flavonoids, which are compounds that have anti-inflammatory properties.
Essential oil applied onto the affected muscles provides relief from spasms. Chamomile tea can also help relax sore muscles.
As a popular remedy, it may be thought of as the European counterpart of ginseng. Chamomile tea benefits the muscles along the digestive tract, allowing
digestion to take place more efficiently. It helps muscles
relax in other parts of the body, which helps people who
suffer from insomnia fall asleep naturally.
The nervous system benefits from Chamomile teathrough its calming effects. Muscles in the body contract and relax in response to chemical signals delivered through the bloodstream. Muscles that are having difficulty relaxing have a chemical in them that is signaling the muscle to contract.
This herbal muscle relaxer soothes muscles by increasing certain amino acids. With the way humans depend on their muscle function, it is no wonder muscle pain can be a very uncomfortable situation. Some muscle pain sufferers experience manageable pain only causing stiffness and soreness .
Catnip
Chamomile
Lemongrass

A member of the mint family, catnip is native to much of Europe and Asia and, is widely cultivated all over the world.
The actual plant has velvety grayish-green leaves with white flowers (Catmint, Nepeta faassenii, has lavender flowers and is considered more of a garden ornamental than catnip).
For cats, it is usually sold dried and crumbled.
This preparation has no effect on humans, but extracts of the plant have been used for centuries to soothe any number of ailments.
The active ingredient, which causes unusual behavior in cats, is a volatile oil called nepetalactone, which can be found in the leaves & stem of the plant.
Lemongrass
Lemongrass
Lemongrass

Clary Sage
Lemongrass
Clary Sage

- Home
- Somatic Archeology
- Halotherapy
- Cranio-Sacral Therapy
- Chelation Therapy
- Diabetes Therapy
- Colon Hydrotherapy
- Magnetic Field Therapy
- Hypnosis
- Kinesiology
- Oxygen Therapy
- Lymphatic drainage
- Enzyme therapy
- Detox Therapy
- Cryotherapy
- Reflexotherapy
- Body Wrap Therapy
- Colon Hydrotherapy
- Ancient Chinese Medicine
- SPA Treatments
- Visceral Manipulation
- Pelotherapy
- Services
- Our Proposal
- Human Infrastructure
CenterforAncientAlchemyandTheHealingArts
Copyright © 2022 CenterforAncientAlchemyandTheHealingArts - All Rights Reserved.
Powered by GoDaddy Website Builder
